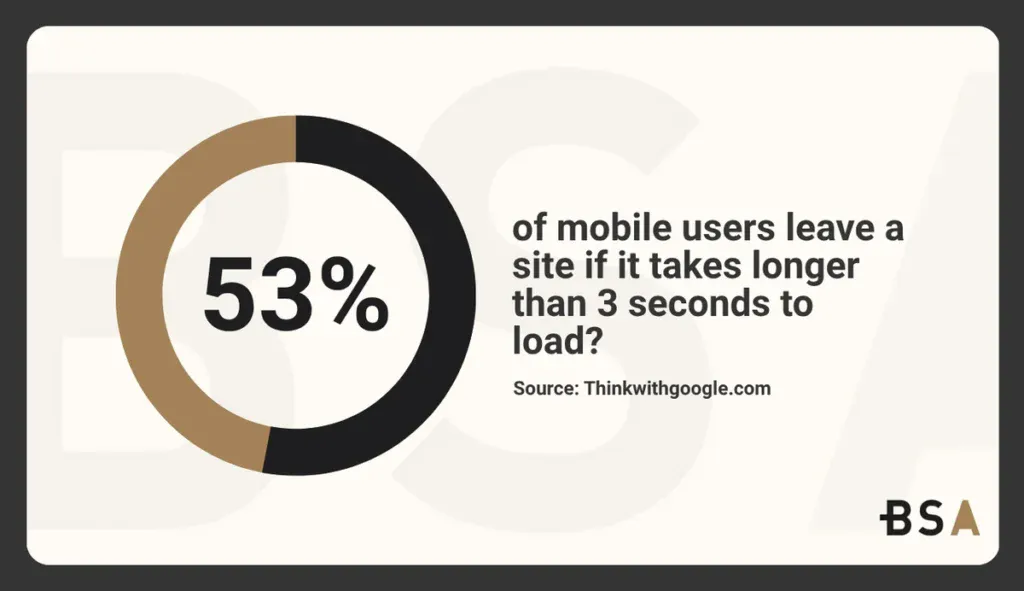
Did you know that 53% of mobile users leave a site if it takes longer than 3 seconds to load? This is just one of the many reasons why having a good custom CMS for your website is important. But which one should you choose this year?
When comparing Magento vs WordPress, knowing what you need can make or break your online business’s future. Magento powers roughly 142,000 live websites, while WordPress runs an impressive 35 million.
Magento’s dominance in the EMEA region’s eCommerce world reached 33% of large companies in 2022.
On the contrary, WordPress controls 68% of the global website builder market. This difference exists because each platform serves a unique purpose. Magento drives sales effectively, while WordPress excels at marketing your website or online store.
This article looks at Magento vs WordPress based on user-friendliness, eCommerce features, design options, security, and costs. It aims to help you find the right fit for your online business.
Trying to improve your website but don’t know where to start? Let us help.
Platform Overview: Magento vs WordPress
“Magento vs WordPress which is best?” is a common question we see every week. Both of them are giants in their fields, but they work quite differently at their core. These differences will help you pick the right platform that matches your business goals.
Magento: Built for eCommerce from the ground up
For most people one of the main WordPress alternatives is Magento. It launched in 2008 as a dedicated eCommerce platform specifically built for online selling. This eCommerce-specific composable platform lets merchants launch stores quickly and spend less on ownership. Its design focuses on advanced shopping features rather than trying to modernize commerce features onto a content system.
The platform comes packed with powerful features right from the start.
You’ll find multi-store management, advanced inventory control, and customer segmentation tools. These built-in features make Magento a great choice for businesses with complex selling needs.
Adobe’s purchase in 2018 split the platform into two options. Many businesses opt for the free Magento Open Source version.
But Adobe Commerce, the paid version, gives access to enterprise-level features and cloud-based infrastructure. This setup shows how Magento serves businesses of all sizes with different resource needs.
WordPress: A CMS with eCommerce capabilities via plugins
WordPress began its story in 2003 as a blogging platform and grew into a complete content management system.
Unlike Magento, WordPress doesn’t come with built-in eCommerce features. It uses plugins like WooCommerce to turn the platform into a powerful online store.
This plugin-based approach gives WordPress amazing flexibility. The platform now runs 43% of the internet, showing how well it works for different types of websites. WooCommerce has powered over 4 million online stores.
This makes it a top choice in the eCommerce space worldwide.
WordPress’s design puts content creation first, adding commerce features when needed. This approach is great for content-driven eCommerce. Blogs, product stories, and marketing content are key parts.
WordPress offers over 59,000 plugins, while Magento has 4,000 extensions. This shows that WordPress has a clear advantage in customization options.
Magento vs WordPress: Key architectural differences
The 2015 release of Magento 2 wasn’t just an update; it was a complete platform rebuild. This new design brought advanced indexers that make store performance and data handling much better.
Magento 2 can handle large order volumes and manage inventories of up to 600,000 products. This shows its strong enterprise-level capabilities.
WordPress takes a different approach with its modular design that grows with your needs.
Instead of using lots of resources by default, WordPress lets you build exactly what you want through its plugin system.
Developers must know PHP to work with Magento, which makes it harder for non-developers to use. WordPress offers a more user-friendly approach. you can use basic features without any coding knowledge. This difference changes how much time and money you’ll spend on development.
Both platforms come with built-in REST APIs that let you create custom applications. Magento uses more server resources because of its complete eCommerce architecture, so you’ll spend more on hosting as your store grows.
Security also sets these platforms apart. Magento builds security into its core design with stronger built-in protections. WordPress needs extra plugins for similar security but excels at content marketing with its native blogging features and many SEO plugin choices.
Many businesses prefer Magento for complex, high-volume eCommerce. It handles large operations well.
On the other hand, WordPress is better for content-rich stores. It offers more marketing flexibility and focuses less on built-in commerce features.
Ease of Use and Learning Curve
The learning curve between Magento and WordPress is one of the main factors that will affect your platform choice for eCommerce.
New users quickly notice how different these platforms are to learn and master.
Installation process: One-click vs manual setup
WordPress shines with its simple installation. Many hosting providers let you install WordPress with just one click. You can set up your site in under five minutes. Bluehost, which WordPress officially recommends, has free one-click installation with every new account.
The platform greets you with a clean interface and quick options to create your blog.
Magento takes a different path and needs technical know-how to set up. You’ll need coding skills (PHP, XML, MySQL), especially if you want custom designs.
The process involves downloading Magento software, creating a database, setting up a web server like Apache or Nginx, and several technical steps.
Some hosts like SiteGround try to make it easier, but their instructions still target developers.
Admin dashboard usability for non-developers
WordPress welcomes everyone with an accessible interface and a clear navigation menu. The left-side menu gives you quick access to Posts, Pages, Media, Comments, Appearance, Plugins, Users, and Settings.
Magento’s admin panel puts you in control with options like Dashboard, Sales, Catalog, Customers, Marketing, Content, Reports, and System. The interface packs more technical features that take time to understand.
The good news is that once you learn it, Magento becomes a powerhouse. You can create products with thousands of variations in minutes.
Explore how we boosted Blue Fin Group’s user engagement by 23.6% with a custom website in our latest case study.
Developer-friendliness and customization flexibility
These platforms let you customize extensively but in different ways. Magento gives you almost unlimited potential to modify your store through development and extensions. This helps create a store that fits exact business needs.
The catch is that design changes often need coding skills, so many businesses hire developers for custom layouts.
WordPress makes life easier for developers. It’s more welcoming to those who want to build new features, and newcomers can start contributing quickly.
This open approach has created a larger community of developers. They provide support, tutorials, and ready-made solutions.
WordPress users can choose from over 13,000 themes and countless plugins for almost anything. Magento has a few hundred themes on its Marketplace and from other providers. Most Magento extensions cost money and need developer help to set up properly.
Both platforms let you build third-party applications through REST APIs. WordPress simplifies customization with user-friendly page builders like Elementor and Beaver Builder. You don’t need much coding to use them.
Your choice between these platforms often depends on your resources.
Think about whether you have developers on hand or want a platform that you can manage yourself.
Magento vs WordPress: eCommerce Capabilities and Scalability
The gap between Magento and WordPress becomes clear when you look at their eCommerce features and how well they grow with your business.
These differences help determine which platform best fits your online store’s needs.
Built-in eCommerce features: Magento vs WooCommerce
Magento comes with detailed eCommerce features built into its core design. The platform has advanced inventory management, flexible pricing rules, and sophisticated product setup options without extra extensions. Merchants who sell complex items can use simple, configurable, grouped, bundled, and virtual products from day one.
WordPress started as a content management system and doesn’t have built-in eCommerce features.
Store owners must add WooCommerce or similar plugins to sell online. This plugin approach works well for many businesses, and WooCommerce now runs more than 3 million live websites.
Magento stands out with built-in customer segmentation, advanced product attributes, layered navigation, and multi-source inventory management. Its attribute sets help create products quickly and offer detailed filtering options.
The platform offers a configurable search feature. It includes auto-suggested terms and breadcrumbs for easy navigation.
WooCommerce makes up for WordPress’s lack of native eCommerce through many plugin options. Its ecosystem provides solutions for digital downloads, memberships, subscriptions, and marketplace selling. This reliance on plugins can cause compatibility issues, extra costs, and slower websites.
Handling large product catalogs and high traffic
Businesses with large inventories will find Magento’s capabilities superior. The platform handles over 100,000 products without slowing down and manages complex product catalogs well through proper indexing and database optimization.
Magento’s key scalability features include:
- Full-page caching to improve load times.
- ElasticSearch for faster product searches.
- Block-level caching to reduce server load.
- Optimized checkout processes for quick transactions.
WordPress with WooCommerce supports about 10,000+ products, but it might slow down without good hosting and optimizations. Growing traffic usually means upgrading from shared hosting to VPS or cloud solutions.
Performance differences show up most under heavy load. Magento processes thousands of transactions hourly but needs high-performance hosting and expert setup to work best.
WordPress works well for small-to-medium businesses on standard hosting but needs major optimization for large stores.
Multi-store and multi-language support
Magento’s design excels with its resilient multi-store features. Merchants can run multiple storefronts from one admin panel.
You can customize languages, currencies, payment methods, and shipping options for each store.
Magento’s multi-store structure has:
- Websites (top-level with unique domains)
- Stores (mid-level with shared cart functionality)
- Store views (lowest level for language variations)
This setup helps businesses expand globally or target different market segments. Merchants can limit product categories per store, build separate catalogs, and use different pricing while keeping central inventory control.
WordPress needs extra plugins to match these multi-store features. WordPress can scale nicely with the right setup. However, it needs more extensions to match Magento’s built-in multi-store features.
Your current needs and future growth plans should guide your platform choice. Magento needs more original investment but scales better for ambitious eCommerce projects.
Themes, Plugins, and Design Flexibility
Your online store’s look and feel depend on the design elements and extensions your chosen platform offers. WordPress and Magento differ a lot in what they let you customize.
Theme availability and customization options
These platforms are worlds apart when it comes to themes. WordPress gives you access to over 13,000 free themes in its official directory, plus thousands of premium options in various marketplaces. You can customize these themes extensively with page builders like Elementor and Beaver Builder, even if you don’t know much code.
Magento keeps things minimal with just two default design themes, Luma for demos and Blank for custom development. Their marketplace has only 11 themes, though you can find more premium options on other sites.
What Magento lacks in numbers, it makes up for with powerful architecture. Its themes handle big catalogs and complex stores better.
WordPress themes cost anywhere from free to USD 200 for premium versions. Magento themes are pricier, starting at USD 50 and going up to several hundred dollars. Some advanced custom themes can cost more than USD 10,000.
Plugin ecosystems: 60,000+ WordPress vs 4,000+ Magento
Plugin numbers show one of the biggest gaps between these platforms. WordPress has an amazing 59,000+ free and paid plugins that cover pretty much everything you’d want to do with a website. This includes tons of WooCommerce add-ons for payments, marketing, shipping, and customer management.
Magento’s marketplace has about 4,400 extensions for its Open Source version. Though fewer, these extensions focus on specific eCommerce needs like accounting, marketing, payments, and security. They cost more too, from a few dollars to thousands, and often need command-line knowledge to install.
Both platforms let you build custom plugins. WordPress makes this easier for developers at all skill levels. Business owners can save money and time with WordPress compared to Magento.
Headless commerce and PWA support
Modern stores work differently now thanks to headless commerce and Progressive Web Apps (PWAs). Magento shines here with strong headless features that separate the frontend from the backend.
Magento store owners can:
- Build frontends with modern tools like React, Vue.js, and Next.js.
- Create interfaces that work perfectly on any device.
- Use PWA Studio for mobile experiences that feel like native apps.
- Let customers use the store offline and receive push notifications..
WordPress can do headless too, but you will need extra setup since it is not built-in.
Magento PWA themes load super fast, work offline, and let customers add your store to their home screen. These features make Magento great for businesses focused on mobile shopping and global markets.
Your choice comes down to what matters more: WordPress’s huge ecosystem of design options or Magento’s specialized eCommerce themes and progressive web features.
Learn how we increased Rao’s Homemade conversion rate by 62% after a website redesign in our recent case study.
Security, SEO, and Performance
Security, SEO, and performance capabilities are the foundations of any successful eCommerce operation.
Each platform offers unique approaches to these vital elements.
Security features: PCI compliance, 2FA, and plugin risks
Magento’s resilient security measures run throughout its architecture. The platform works exceptionally well for businesses that handle sensitive customer information. It has built-in PCI compliance features, two-factor authentication, and advanced admin security settings.
These elements protect payment data effectively, which are crucial for stores that process credit card information directly.
WordPress handles security differently and relies mostly on third-party plugins and proper setup. Unlike Magento’s built-in protections, WordPress security largely depends on updated plugins.
Yet only 48% of WordPress websites run current versions. This update gap creates vulnerabilities that store owners must actively manage.
When comparing Magento vs WordPress, both platforms come with unique security challenges. Magento’s security updates need manual installation through command-line operations. This creates a technical hurdle for many store owners.
WordPress can schedule security updates automatically, but unverified third-party plugins still pose major risks without proper vetting.
Store owners who prioritize payment security will find several advantages with Magento. Its security features have:
- Regular updates that fix vulnerabilities.
- Built-in PCI compliance tools.
- Two-factor authentication options.
- Firewalls and risk monitoring capabilities.
SEO tools: Built-in vs plugin-based optimization
Magento 2 comes with several built-in SEO features made specifically for eCommerce. WordPress gives more SEO flexibility through its vast plugin ecosystem.
Magento’s native SEO tools have meta tags, mobile-friendly site designs, improved search engine features, XML sitemaps, plus alt tags, and image optimization. Store owners can create SEO-optimized shops without extra extensions. Magento supports structured data markup. It uses default templates for rich product listings in search results.
WordPress needs SEO plugins but shines with options like Yoast SEO. These tools provide user-friendly dashboards for on-page and off-page optimization. Users get readability guidance alongside technical SEO features that work well for both beginners and experts.
Each platform’s origins shape their SEO approach. Magento focuses on product-centric SEO since it’s built for eCommerce. WordPress is great for content marketing SEO. It offers easy ways to customize meta-descriptions, SEO titles, and image alt-text.
Performance under load: Caching, CDN, and speed
Store size and traffic make performance differences more obvious. Magento has several built-in caching tools like Varnish, Full Page Cache, Redis, and Memcached. Large stores can maintain good loading speeds even with heavy traffic using these technologies.
Both platforms work better with Content Delivery Networks (CDNs). A well-set CDN boosts security against attacks and serves an even bigger purpose – it spreads data geographically to speed up content delivery. Stores serving global customers benefit greatly from this feature.
Magento usually needs more hosting resources than WordPress and works best with VPS or dedicated servers. The platform stays resource-heavy even with proper setup. WordPress runs well on simpler hosting for smaller stores but needs extensive optimization for large catalogs.
Magento’s architecture supports Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) that provide app-like mobile experiences with offline features. This becomes more valuable as mobile commerce grows worldwide.
Your choice between Magento and WordPress should match your current security needs, SEO strategy complexity, and expected performance requirements as your store expands.
Both platforms offer viable solutions with different resource needs and technical skill requirements.
Magento vs WordPress: Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Your choice between eCommerce platforms depends on how much you’re willing to spend.
WordPress and Magento have different pricing models that show who they’re really built for.
Magento Open Source vs Adobe Commerce pricing
Magento’s pricing works in tiers with clear options. You can download and use Magento Open Source for free, which makes it a good fit for businesses with tight budgets.
All in all, Adobe Commerce (the old Magento Commerce) costs quite a bit more, though. You’ll need at least USD 22,000 per year. The cloud version, Adobe Commerce Cloud, starts at USD 40,000 yearly.
The price differences make sense when you look closer. Adobe Commerce bases its pricing on your store’s Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) and Average Order Value (AOV). Your costs go up as you make more money.
The pricing spreads across five tiers that match yearly revenue. From stores making under USD 1 million to those bringing in over USD 25 million.
Hidden costs: Hosting, themes, plugins, and developer fees
License fees are just the start. There are many more costs to think about. Hosting needs are different too. Magento needs strong servers that cost USD 100-850 monthly, depending on your traffic. WordPress runs fine on simpler hosting plans at USD 5-50 monthly.
Themes tell a similar story. WordPress themes cost anywhere from free to USD 200. Magento themes are pricier, costing USD 60 to USD 600 for regular options.
Custom designs might set you back USD 10,000.
Developer costs are the biggest variable. North American Magento developers charge USD 50-120 per hour, with specialist architects asking USD 300-500 hourly. WordPress developers are easier on the wallet at USD 40-80 per hour. This difference exists because WordPress doesn’t require as much technical know-how for simple setups.
Keeping your site running smoothly is another vital cost. Even with Magento Open Source’s free license, you’ll likely spend USD 10,000-40,000 yearly on support. WordPress maintenance packages are cheaper, ranging from USD 380-1,250 monthly.
Get a Custom Website That Converts With Blacksmith
The choice when comparing Magento vs WordPress directly impacts your business goals, technical abilities, and budget. These platforms serve different purposes, even though both can power your online store.
But let’s face it, creating a website with either platform is a project that will take weeks, if not months, to properly finish. This is without even adding all the extra work needed to properly maintain your website. This is time you could be using on other aspects of your business. So what now?
That’s where we come in. Blacksmith is a premium web development agency with a group of seasoned web developers ready to create the perfect website for your business. Be it with Magento or WordPress, we’ll ensure your business stands out from your competitors and performs year-round.
Unsure if investing in a custom website is what your business needs? Don’t worry, click here to schedule a call with us and we’ll provide you with a brand audit. This way, we can show you all the areas where you’re losing potential clients and what we do to help you fix it.